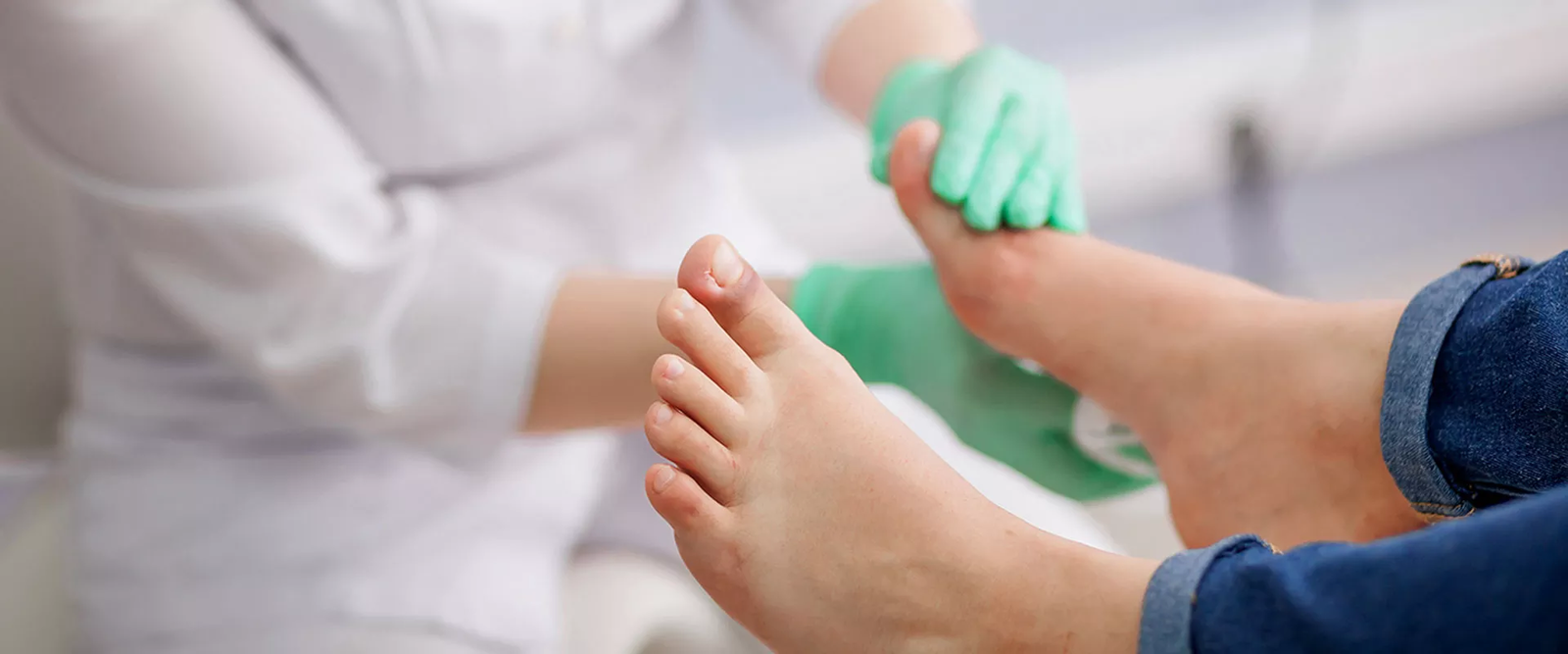

Diabetic foot is a complication that can appear in different types. Here are the most common types of diabetic foot:
Diabetic Neuropathic Foot: This type develops due to nerve damage and may cause symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and burning in the feet. This condition makes it difficult to notice injuries and prolongs the healing process.
Ischemic Foot: It occurs due to problems in blood circulation, resulting in insufficient oxygen delivery to the feet. This condition can cause non-healing wounds and foot ulcers.
Infected Foot: Diabetic foot ulcers carry a risk of infection. Untreated infected wounds may lead to serious complications and tissue loss.
Non-healing Foot Ulcers: Deepening and non-healing wounds can damage underlying tissues and bones. Sometimes this may require amputation.
Causes of Diabetic Foot
Many factors play a role in the development of diabetic foot. These include:
High Blood Sugar Levels: Prolonged high blood sugar can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and circulation problems.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): Causes loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to notice wounds.
Circulatory Problems: Insufficient blood flow hinders oxygen and nutrient delivery, delaying healing.
Foot Deformities: Foot shape abnormalities affect pressure points, increasing the risk of injury.
Inadequate Foot Care: Lack of regular hygiene and improper shoe selection increases injury risk.
How Diabetic Foot Ulcers Form
Diabetic foot ulcers form as a result of the following factors coming together:
High sugar levels causing nerve damage and circulation problems.
Nerve damage (neuropathy) causing unnoticed injuries.
Circulatory problems prolonging healing time and deepening wounds.
Wrong shoe choice: tight and narrow shoes can cause injuries.
Symptoms of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Redness, swelling, or wounds on the foot,
Numbness or tingling,
Necrosis (tissue death).
Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetic foot care is vital both to prevent wounds and to stop the progression of existing wounds.
Daily Foot Inspection: Check your feet every day for cuts, wounds, or redness.
Foot Cleaning: Wash with lukewarm water and dry thoroughly.
Moisturizing: Keep the skin soft but avoid applying moisturizer between toes.
Nail Care: Regularly trim and file your nails.
Appropriate Shoe Selection: Prefer comfortable, soft, and properly sized shoes.
Diabetes Control: Regularly monitor your blood sugar to minimize complications.
Regular Exercise: Exercise regularly to improve blood circulation in your feet.
Early diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot increase quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. You can achieve better outcomes by cooperating with your diabetes care team.